1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| lrmf_a <- paste0("factor(dcf_status)~", paste(colnames(df)[1:9], collapse = '+'))
lrmf_b <- paste0("factor(dcf_status)~", paste(colnames(df)[1:10], collapse = '+'))
fit_A <- glm(formula(lrmf_a), data = df, family = binomial(link="logit"), x=TRUE)
fit_B <- glm(formula(lrmf_b), data = df, family = binomial(link="logit"), x=TRUE)
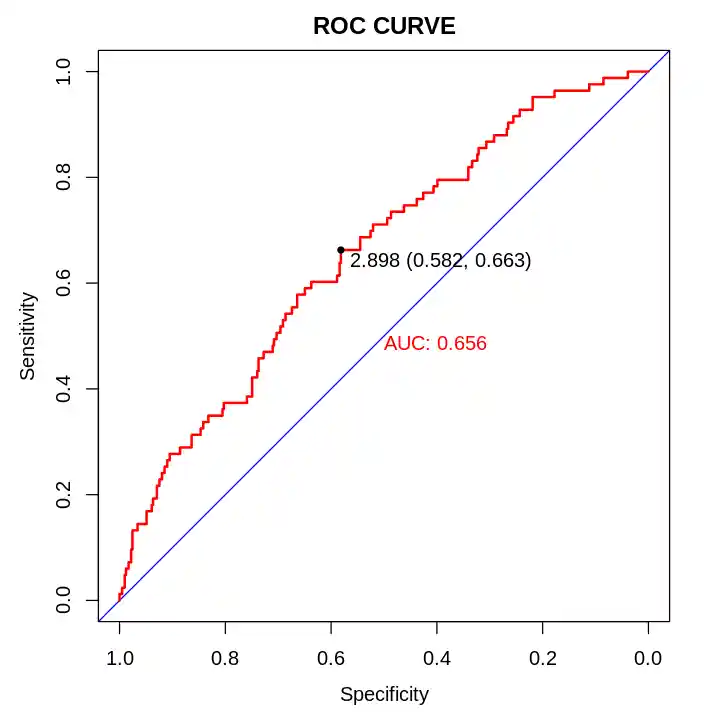
gfit <- roc(factor(dcf_status)~predict(fit_A), data = df)
options(repr.plot.width=10, repr.plot.height=10)
plot(gfit,
print.auc=TRUE,
print.thres=TRUE,
main = "ROC CURVE",
col= "red",
print.thres.col="black",
identity.col="blue",
identity.lty=1,identity.lwd=1)
NRI <- nribin(mdl.std = fit_A, mdl.new = fit_B,
updown = 'diff',
cut = 0.05, niter = 500, alpha = 0.05)
NRI <- nribin(mdl.std = fit_A, mdl.new = fit_B,
updown = 'category',
cut = 1.791, niter = 500, alpha = 0.05)
|