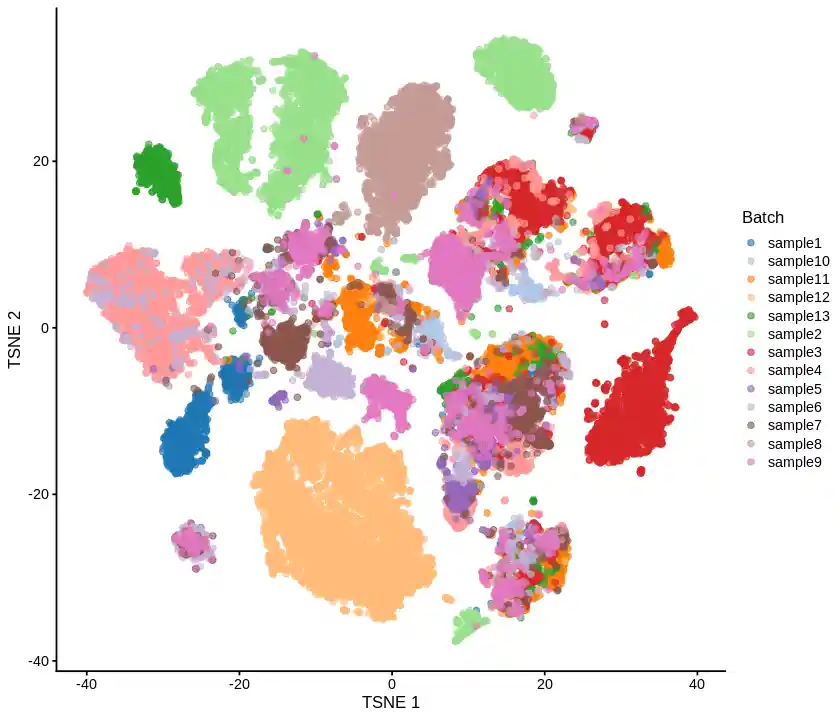
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| library(scran);
library(Seurat);
library(scater);
library(batchelor);
sce <- readRDS('clustered_normalized.rds')
batch <- as.numeric(as.factor(sce$batch));
count1 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 1];
count2 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 2];
count3 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 3];
count4 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 4];
count5 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 5];
count6 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 6];
count7 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 7];
count8 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 8];
count9 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 9];
count10 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 10];
count11 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 11];
count12 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 12];
count13 <- logcounts(sce)[, batch == 13, drop = FALSE];
original <- list(count1, count2, count3, count4, count5, count6, count7, count8,
count9, count10, count11, count12, count13);
names(original) <- levels(as.factor(as.factor(sce$batch)))
gc()
system(paste("python3 /home/jovyan/upload/zl_liu/wecomchan.py", "'fastMNN_task start'"), intern = T)
out <- tryCatch({
do.call(fastMNN, c(original, list(k = 20, d = 50, BPPARAM = BiocParallel::MulticoreParam(6))));
}, warning = function(w) {
w <- as.character(w)
w <- gsub("[\r\n']", "", w)
system(paste("python3 /home/jovyan/upload/zl_liu/wecomchan.py", paste0("'",w,"'")), intern = T)
w
}, error = function(e) {
e <- as.character(e)
e <- gsub("[\r\n']", "", e)
system(paste("python3 /home/jovyan/upload/zl_liu/wecomchan.py", paste0("'",e,"'")), intern = T)
e
}, finally = {
})
system(paste("python3 /home/jovyan/upload/zl_liu/wecomchan.py", "'fastMNN completed'"), intern = T)
|